VES Application User Guide¶
The Barometer repository contains a python based application for VES (VNF Event Stream) which receives the collectd specific metrics via Kafka bus, normalizes the metric data into the VES message format and sends it into the VES collector.
The application currently supports pushing platform relevant metrics through the additional measurements field for VES.
Collectd has a write_kafka plugin that sends collectd metrics and values to
a Kafka Broker. The VES message formatting application, ves_app.py, receives metrics from
the Kafka broker, normalises the data to VES message format for forwarding to VES collector.
The VES message formatting application will be simply referred to as the “VES application”
within this userguide
The VES application can be run in host mode (baremetal), hypervisor mode (on a host with a hypervisor and VMs running) or guest mode(within a VM). The main software blocks that are required to run the VES application demo are:
- Kafka
- Collectd
- VES Application
- VES Collector
Install Kafka Broker¶
Dependencies: install JAVA & Zookeeper.
Ubuntu 16.04:
$ sudo apt-get install default-jre $ sudo apt-get install zookeeperd $ sudo apt-get install python-pip
CentOS:
$ sudo yum update -y $ sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk $ sudo yum install epel-release $ sudo yum install python-pip $ sudo yum install zookeeper $ sudo yum install telnet $ sudo yum install wget
Note
You may need to add the repository that contains zookeeper. To do so, follow the step below and try to install zookeeper again using steps above. Otherwise, skip next step.
$ sudo yum install https://archive.cloudera.com/cdh5/one-click-install/redhat/7/x86_64/cloudera-cdh-5-0.x86_64.rpm
Start zookeeper:
$ sudo zookeeper-server start
if you get the error message like
ZooKeeper data directory is missing at /var/lib/zookeeperduring the start of zookeeper, initialize zookeeper data directory using the command below and start zookeeper again, otherwise skip the next step.$ sudo /usr/lib/zookeeper/bin/zkServer-initialize.sh No myid provided, be sure to specify it in /var/lib/zookeeper/myid if using non-standalone
Test if Zookeeper is running as a daemon.
$ telnet localhost 2181
Type ‘ruok’ & hit enter. Expected response is ‘imok’ which means that Zookeeper is up running.
Install Kafka
Note
VES doesn’t work with version 0.9.4 of kafka-python. The recommended/tested version is 1.3.3.
$ sudo pip install kafka-python $ wget "https://archive.apache.org/dist/kafka/1.0.0/kafka_2.11-1.0.0.tgz" $ tar -xvzf kafka_2.11-1.0.0.tgz $ sed -i -- 's/#delete.topic.enable=true/delete.topic.enable=true/' kafka_2.11-1.0.0/config/server.properties $ sudo nohup kafka_2.11-1.0.0/bin/kafka-server-start.sh \ kafka_2.11-1.0.0/config/server.properties > kafka_2.11-1.0.0/kafka.log 2>&1 &
Note
If Kafka server fails to start, please check if the platform IP address is associated with the hostname in the static host lookup table. If it doesn’t exist, use the following command to add it.
$ echo "$(ip route get 8.8.8.8 | awk '{print $NF; exit}') $HOSTNAME" | sudo tee -a /etc/hostsTest the Kafka Installation
To test if the installation worked correctly there are two scripts, producer and consumer scripts. These will allow you to see messages pushed to broker and receive from broker.
Producer (Publish “Hello World”):
$ echo "Hello, World" | kafka_2.11-1.0.0/bin/kafka-console-producer.sh \ --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic TopicTest > /dev/null
Consumer (Receive “Hello World”):
$ kafka_2.11-1.0.0/bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --zookeeper \ localhost:2181 --topic TopicTest --from-beginning --max-messages 1 --timeout-ms 3000
Install collectd¶
Install development tools:
Ubuntu 16.04:
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential bison autotools-dev autoconf $ sudo apt-get install pkg-config flex libtoolCentOS:
$ sudo yum group install 'Development Tools'
Install Apache Kafka C/C++ client library:
$ git clone https://github.com/edenhill/librdkafka.git ~/librdkafka
$ cd ~/librdkafka
$ git checkout -b v0.9.5 v0.9.5
$ ./configure --prefix=/usr
$ make
$ sudo make install
Build collectd with Kafka support:
$ git clone https://github.com/collectd/collectd.git ~/collectd
$ cd ~/collectd
$ ./build.sh
$ ./configure --with-librdkafka=/usr --without-perl-bindings --enable-perl=no
$ make && sudo make install
Note
If installing from git repository collectd.conf configuration file will be located in
directory /opt/collectd/etc/. If installing from via a package manager collectd.conf
configuration file will be located in directory /etc/collectd/
Configure and start collectd. Modify Collectd configuration file collectd.conf
as following:
- Within a VM: Setup VES application (guest mode)
- On Host with VMs: Setup VES application (hypervisor mode)
- No Virtualization: Setup VES application (host mode)
Start collectd process as a service as described in Installing collectd as a service.
Setup VES application (guest mode)¶
In this mode Collectd runs from within a VM and sends metrics to the VES collector.
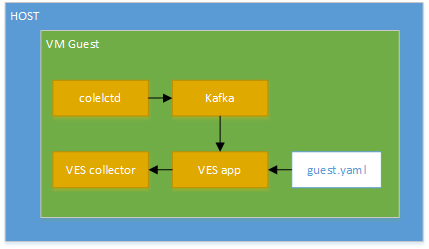
VES guest mode setup
Install dependencies:
$ sudo pip install pyyaml python-kafka
Clone Barometer repo and start the VES application:
$ git clone https://gerrit.opnfv.org/gerrit/barometer
$ cd barometer/3rd_party/collectd-ves-app/ves_app
$ nohup python ves_app.py --events-schema=guest.yaml --config=ves_app_config.conf > ves_app.stdout.log &
Modify Collectd configuration file collectd.conf as following:
LoadPlugin logfile LoadPlugin interface LoadPlugin memory LoadPlugin load LoadPlugin disk LoadPlugin uuid LoadPlugin write_kafka <Plugin logfile> LogLevel info File "/opt/collectd/var/log/collectd.log" Timestamp true PrintSeverity false </Plugin> <Plugin cpu> ReportByCpu true ReportByState true ValuesPercentage true </Plugin> <Plugin write_kafka> Property "metadata.broker.list" "localhost:9092" <Topic "collectd"> Format JSON </Topic> </Plugin>
Start collectd process as a service as described in Installing collectd as a service.
Note
The above configuration is used for a localhost. The VES application can be
configured to use remote VES collector and remote Kafka server. To do
so, the IP addresses/host names needs to be changed in collector.conf
and ves_app_config.conf files accordingly.
Setup VES application (hypervisor mode)¶
This mode is used to collect hypervisor statistics about guest VMs and to send those metrics into the VES collector. Also, this mode collects host statistics and send them as part of the guest VES message.
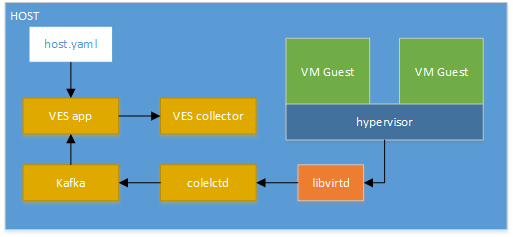
VES hypervisor mode setup
Running the VES in hypervisor mode looks like steps described in Setup VES application (guest mode) but with the following exceptions:
- The
hypervisor.yamlconfiguration file should be used instead ofguest.yamlfile when VES application is running. - Collectd should be running on hypervisor machine only.
- Addition
libvirtddependencies needs to be installed on where collectd daemon is running. To install those dependencies, see virt plugin section of Barometer user guide. - The next (minimum) configuration needs to be provided to collectd to be able to generate the VES message to VES collector.
Note
At least one VM instance should be up and running by hypervisor on the host.
LoadPlugin logfile
LoadPlugin cpu
LoadPlugin virt
LoadPlugin write_kafka
<Plugin logfile>
LogLevel info
File "/opt/collectd/var/log/collectd.log"
Timestamp true
PrintSeverity false
</Plugin>
<Plugin virt>
Connection "qemu:///system"
RefreshInterval 60
HostnameFormat uuid
PluginInstanceFormat name
ExtraStats "cpu_util"
</Plugin>
<Plugin write_kafka>
Property "metadata.broker.list" "localhost:9092"
<Topic "collectd">
Format JSON
</Topic>
</Plugin>
Start collectd process as a service as described in Installing collectd as a service.
Note
The above configuration is used for a localhost. The VES application can be
configured to use remote VES collector and remote Kafka server. To do
so, the IP addresses/host names needs to be changed in collector.conf
and ves_app_config.conf files accordingly.
Note
The list of the plugins can be extented depends on your needs.
Setup VES application (host mode)¶
This mode is used to collect platform wide metrics and to send those metrics into the VES collector. It is most suitable for running within a baremetal platform.
Install dependencies:
$ sudo pip install pyyaml
Clone Barometer repo and start the VES application:
$ git clone https://gerrit.opnfv.org/gerrit/barometer
$ cd barometer/3rd_party/collectd-ves-app/ves_app
$ nohup python ves_app.py --events-schema=host.yaml --config=ves_app_config.conf > ves_app.stdout.log &
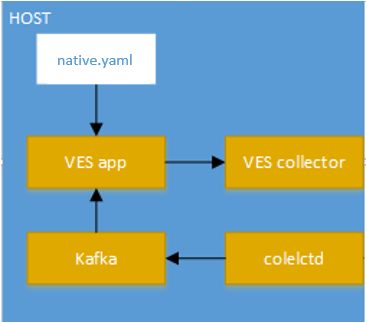
VES Native mode setup
Modify collectd configuration file collectd.conf as following:
LoadPlugin interface
LoadPlugin memory
LoadPlugin disk
LoadPlugin cpu
<Plugin cpu>
ReportByCpu true
ReportByState true
ValuesPercentage true
</Plugin>
LoadPlugin write_kafka
<Plugin write_kafka>
Property "metadata.broker.list" "localhost:9092"
<Topic "collectd">
Format JSON
</Topic>
</Plugin>
Start collectd process as a service as described in Installing collectd as a service.
Note
The above configuration is used for a localhost. The VES application can be
configured to use remote VES collector and remote Kafka server. To do
so, the IP addresses/host names needs to be changed in collector.conf
and ves_app_config.conf files accordingly.
Note
The list of the plugins can be extented depends on your needs.
Setup VES Test Collector¶
Note
Test Collector setup is required only for VES application testing purposes.
Install dependencies:
$ sudo pip install jsonschema
Clone VES Test Collector:
$ git clone https://github.com/att/evel-test-collector.git ~/evel-test-collector
Modify VES Test Collector config file to point to existing log directory and schema file:
$ sed -i.back 's/^\(log_file[ ]*=[ ]*\).*/\1collector.log/' ~/evel-test-collector/config/collector.conf
$ sed -i.back 's/^\(schema_file[ ]*=.*\)event_format_updated.json$/\1CommonEventFormat.json/' ~/evel-test-collector/config/collector.conf
Start VES Test Collector:
$ cd ~/evel-test-collector/code/collector
$ nohup python ./collector.py --config ../../config/collector.conf > collector.stdout.log &
VES application configuration description¶
Details of the Vendor Event Listener REST service
REST resources are defined with respect to a ServerRoot:
ServerRoot = https://{Domain}:{Port}/{optionalRoutingPath}
REST resources are of the form:
{ServerRoot}/eventListener/v{apiVersion}`
{ServerRoot}/eventListener/v{apiVersion}/{topicName}`
{ServerRoot}/eventListener/v{apiVersion}/eventBatch`
Within the VES directory (3rd_party/collectd-ves-app/ves_app) there is a
configuration file called ves_app_conf.conf. The description of the
configuration options are described below:
- Domain “host”
- VES domain name. It can be IP address or hostname of VES collector
(default:
127.0.0.1) - Port port
- VES port (default:
30000) - Path “path”
- Used as the “optionalRoutingPath” element in the REST path (default:
vendor_event_listener) - Topic “path”
- Used as the “topicName” element in the REST path (default:
example_vnf) - UseHttps true|false
- Allow application to use HTTPS instead of HTTP (default:
false) - Username “username”
- VES collector user name (default: empty)
- Password “passwd”
- VES collector password (default: empty)
- SendEventInterval interval
- This configuration option controls how often (sec) collectd data is sent to
Vendor Event Listener (default:
20) - ApiVersion version
- Used as the “apiVersion” element in the REST path (default:
3) - KafkaPort port
- Kafka Port (Default
9092) - KafkaBroker host
- Kafka Broker domain name. It can be an IP address or hostname of local or remote server
(default:
localhost)
VES YAML configuration format¶
The format of the VES message is generated by the VES application based on the
YAML schema configuration file provided by user via --events-schema
command-line option of the application.
Note
Use --help option of VES application to see the
description of all available options
Note
The detailed installation guide of the VES application is described in the VES Application User Guide.
The message defined by YAML schema should correspond to format defined in VES shema definition.
Warning
This section doesn’t explain the YAML language itself, so the knowledge of the YAML language is required before continue reading it!
Since, the VES message output is a JSON format, it’s recommended to understand how YAML document is converted to JSON before starting to create a new YAML definition for the VES. E.g.:
The following YAML document:
---
additionalMeasurements:
plugin: somename
instance: someinstance
will be converted to JSON like this:
{
"additionalMeasurements": {
"instance": "someinstance",
"plugin": "somename"
}
}
Note
The YAML syntax section of PyYAML documentation can be used as a reference for this.
VES message types¶
The VES agent can generate two type of messages which are sent to the VES collector. Each message type must be specified in the YAML configuration file using a specific YAML tag.
- Measurements
This type is used to send a message defined in YAML configuration to the VES collector with a specified interval (default is 20 sec and it’s configurable via command line option of the application). This type can be specified in the configuration using
!Measurementstag. For instance:--- # My comments My Host Measurements: !Measurements ... # message definition
- Events
This type is used to send a message defined in YAML configuration to the VES collector when collectd notification is received from Kafka bus (collectd
write_kafkaplugin). This type can be specified in the configuration using!Eventstag. For instance:--- # My comments My Events: !Events ... # event definition
Collectd metrics in VES¶
The VES application caches collectd metrics received via Kafka bus. The data is stored in a table format. It’s important to know it before mapping collectd metric values to message defined in YAML configuration file.
VES collectd metric cache example:
| host | plugin | plugin_instance | type | type_instace | time | value | ds_name | interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| localhost | cpu | percent | user | 1509535512.30567 | 16 | value | 10 | |
| localhost | memory | memory | free | 1509535573.448014 | 798456 | value | 10 | |
| localhost | interface | eth0 | if_packets | 1509544183.956496 | 253 | rx | 10 | |
| 7ec333e7 | virt | Ubuntu-12.04.5-LTS | percent | virt_cpu_total | 1509544402.378035 | 0.2 | value | 10 |
| 7ec333e7 | virt | Ubuntu-12.04.5-LTS | memory | rss | 1509544638.55119 | 123405 | value | 10 |
| 7ec333e7 | virt | Ubuntu-12.04.5-LTS | if_octets | vnet1 | 1509544646.27108 | 67 | tx | 10 |
| cc659a52 | virt | Ubuntu-16.04 | percent | virt_cpu_total | 1509544745.617207 | 0.3 | value | 10 |
| cc659a52 | virt | Ubuntu-16.04 | memory | rss | 1509544754.329411 | 4567 | value | 10 |
| cc659a52 | virt | Ubuntu-16.04 | if_octets | vnet0 | 1509544760.720381 | 0 | rx | 10 |
It’s possible from YAML configuration file to refer to any field of any row of
the table via special YAML tags like ValueItem or ArrayItem. See the
Collectd metric reference reference for more details.
Note
The collectd data types file contains map of type to
ds_name field. It can be used to get possible value for ds_name
field. See the collectd data types description for more details on
collectd data types.
Aging of collectd metric¶
If the metric will not be updated by the collectd during the double metric interval time, it will be removed (aged) from VES internal cache.
VES YAML references¶
There are four type of references supported by the YAML format: System, Config, Collectd metric and Collectd notification. The format of the reference is the following:
"{<ref type>.<attribute name>}"
Note
Possible values for <ref type> and <attribute name> are
described in farther sections.
System reference¶
This reference is used to get system statistics like time, date etc. The system
reference (<ref type> = system) can be used in any place of the YAML
configuration file. This type of reference provides the following attributes:
hostname- The name of the host where VES application is running.
id- Unique ID during VES application runtime.
time- Current time in seconds since the Epoch. For example
1509641411.631951. date- Current date in ISO 8601 format,
YYYY-MM-DD. For instance2017-11-02.
For example:
Date: "{system.date}"
Config reference¶
This reference is used to get VES configuration described in VES application
configuration description sectoin. The reference (<ref type> = config)
can be used in any place of the YAML configuration file. This type of reference
provides the following attributes:
interval- Measurements dispatch interval. It referenses to
SendEventIntervalconfiguration of the VES application.
For example:
Interval: "{config.interval}"
Collectd metric reference¶
This reference is used to get the attribute value of collectd metric from the
VES cache. The reference (<ref type> = vl) can be used ONLY inside
Measurements, ValueItem and ArrayItem tags. Using the reference
inside a helper tag is also allowed if the helper tag is located inside the
tag where the reference is allowed (e.g.: ArrayItem). The
<attribute name> name corresponds to the table field name described in
Collectd metrics in VES section. For example:
name: "{vl.type}-{vl.type_instance}"
Collectd notification reference¶
This reference is used to get the attribute value of received collectd
notification. The reference (<ref type> = n) can be used ONLY inside
Events tag. Using the reference inside a helper tag is also allowed if
the helper tag is located inside the Events tag. This type of reference
provides the following attributes:
host- The hostname of received collectd notification.
plugin- The plugin name of received collectd notification.
plugin_instance- The plugin instance of the received collectd notification.
type- The type name of the received collectd notification.
type_instance- The type instance of the received collectd notification.
severity- The severity of the received collectd notification.
message- The message of the received collectd notification.
Note
The exact value for each attribute depends on the collectd plugin which may generate the notification. Please refer to the collectd plugin description document to get more details on the specific collectd plugin.
YAML config example:
sourceId: "{n.plugin_instance}"
Collectd metric mapping YAML tags¶
This section describes the YAML tags used to map collectd metric values in the YAML configuration file.
Measurements tag¶
This tag is a YAML map which is used to define the VES measurement message. It’s allowed to be used multiple times in the document (e.g.: you can define multiple VES messages in one YAML document). This tag works in the same way as ArrayItem tag does and all keys have the same description/rules.
ValueItem tag¶
This tag is used to select a collectd metric and get its attribute value using Collectd metric reference. The type of this tag is a YAML array of maps with the possible keys described below.
SELECT(required)- Is a YAML map which describes the select metric criteria. Each key name of the map must correspond to the table field name described in Collectd metrics in VES section.
VALUE(optional)- Describes the value to be assigned. If not provided, the default
!Number "{vl.value}"expression is used. DEFAULT(optional)- Describes the default value which will be assigned if no metric is selected
by
SELECTcriteria.
ValueItem tag description example:
memoryFree: !ValueItem
- SELECT:
plugin: memory
type: memory
type_instance: rss
- VALUE: !Bytes2Kibibytes "{vl.value}"
- DEFAULT: 0
The tag process workflow is described on the figure below.
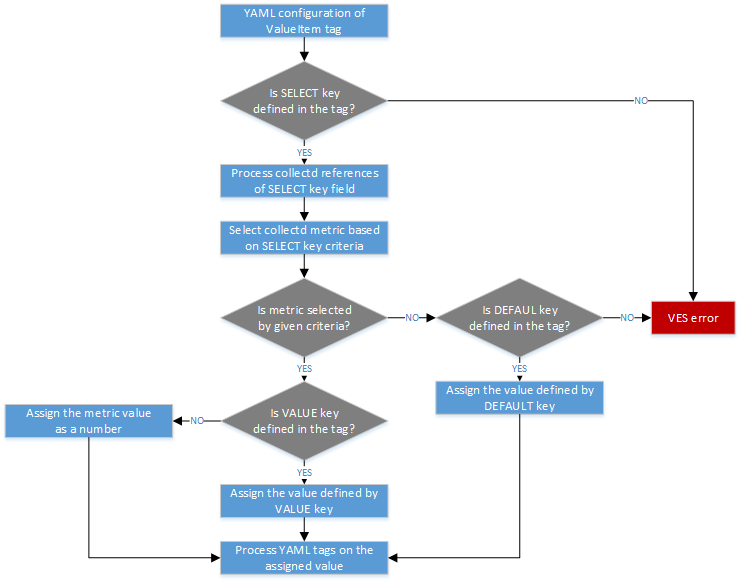
YAML ValueItem tag process workflow
ArrayItem tag¶
This tag is used to select a list of collectd metrics and generate a YAML array
of YAML items described by ITEM-DESC key. If no collectd metrics are
selected by the given criteria, the empty array will be returned.
SELECT(optional)Is a YAML map which describes the select metrics criteria. Each key name of the map must correspond to the table field name described in Collectd metrics in VES section. The value of the key may be regular expression. To enable regular expression in the value, the YAML string containing
/char at the beginning and at the end should be used. For example:plugin: "/^(?!virt).*$/" # selected all metrics except ``virt`` plugin
The VES application uses the python RE library to work with regular expression specified in the YAML configuration. Please refer to python regular expression syntax documentation for more details on a syntax used by the VES.
Multiple
SELECTkeys are allowed by the tag. If norSELECTorINDEX-KEYkey is specified, the VES error is generated.INDEX-KEY(optional)- Is a YAML array which describes the unique fields to be selected by the tag.
Each element of array is a YAML string which should be one of the table field
name described in Collectd metrics in VES section. Please note, if this
key is used, only fields specified by the key can be used as a collectd
reference in the
ITEM-DESCkey. ITEM-DESC(required)- Is a YAML map which describes each element of the YAML array generated by
the tag. Using
ArrayItemtags and other Helper YAML tags are also allowed in the definition of the key.
In the example below, the ArrayItem tag is used to generate an array of
ITEM-DESC items for each collectd metrics except virt plugin with
unique plugin, plugin_instance attribute values.
Measurements: !ArrayItem
- SELECT:
plugin: "/^(?!virt).*$/"
- INDEX-KEY:
- plugin
- plugin_instance
- ITEM-DESC:
name: !StripExtraDash "{vl.plugin}-{vl.plugin_instance}"
The tag process workflow is described on the figure below.
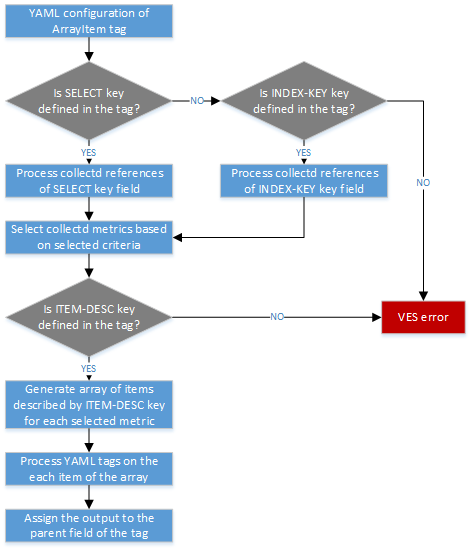
YAML ArrayItem tag process workflow
Collectd event mapping YAML tags¶
This section describes the YAML tags used to map the collectd notification to the VES event message in the YAML configuration file.
Events tag¶
This tag is a YAML map which is used to define the VES event message. It’s allowed to be used multiple times in the document (e.g.: you can map multiple collectd notification into VES message in one YAML document). The possible keys of the tag are described below.
CONDITION(optional)- Is a YAML map which describes the select metric criteria. Each key name of the map must correspond to the name of attribute provided by Collectd notification reference. If no such key provided, any collectd notification will map the defined YAML message.
ITEM-DESC(required)- Is a YAML map which describes the message generated by this tag. Only Helper YAML tags are allowed in the definition of the key.
The example of the VES event message which will be generate by the VES
application when collectd notification of the virt plugin is triggered
is described below.
---
Virt Event: !Events
- ITEM-DESC:
event:
commonEventHeader:
domain: fault
eventType: Notification
sourceId: &event_sourceId "{n.plugin_instance}"
sourceName: *event_sourceId
lastEpochMicrosec: !Number "{n.time}"
startEpochMicrosec: !Number "{n.time}"
faultFields:
alarmInterfaceA: !StripExtraDash "{n.plugin}-{n.plugin_instance}"
alarmCondition: "{n.severity}"
faultFieldsVersion: 1.1
- CONDITION:
plugin: virt
Helper YAML tags¶
This section describes the YAML tags used as utilities for formatting the output message. The YAML configuration process workflow is described on the figure below.
YAML configuration process workflow
Convert string to number tag¶
The !Number tag is used in YAML configuration file to convert string value into
the number type. For instance:
lastEpochMicrosec: !Number "3456"
The output of the tag will be the JSON number.
{
lastEpochMicrosec: 3456
}
Convert bytes to Kibibytes tag¶
The !Bytes2Kibibytes tag is used in YAML configuration file to convert
bytes into kibibytes (1 kibibyte = 1024 bytes). For instance:
memoryConfigured: !Bytes2Kibibytes 4098
memoryConfigured: !Bytes2Kibibytes "1024"
The output of the tag will be the JSON number.
{
memoryConfigured: 4
memoryConfigured: 1
}
Convert one value to another tag¶
The !MapValue tag is used in YAML configuration file to map one value
into another value defined in the configuration. For instance:
Severity: !MapValue
VALUE: Failure
TO:
Failure: Critical
Error: Warnign
The output of the tag will be the mapped value.
{
Severity: Critical
}
Strip extra dash tag¶
The !StripExtraDash tag is used in YAML configuration file to strip extra
dashes in the string (dashes at the beginning, at the end and double dashes).
For example:
name: !StripExtraDash string-with--extra-dashes-
The output of the tag will be the JSON string with extra dashes removed.
{
name: string-with-extra-dashes
}
Limitations¶
- Only one document can be defined in the same YAML configuration file.
- The collectd notification is not supported by Kafka collectd plugin. Due to this limitation, the collectd notifications cannot be received by the VES application and the defined YAML event will not be generated and sent to the VES collector. Please note, that VES YAML format already supports the events definition and the format is descibed in the document.
